2013-03-22, 12:07
Lets get this out of the way, GITHub is awesome but the learning curve is crazy hard.


Here's a little guide to starting off from the perspective of a n00b while attempting to put it in plain English.
I'm assuming you have signed up for github and are working on Windows with TortoiseGIT installed. Other platforms and Git tools should work in a similar way.
Cloning a Repository
Copying an existing project from the GITHub website and all its code to your local computer.
This is usually used when you want to test a one time copy of a project on your local computer without making any changes in the future
1) Create a folder on your computer for the projects to be stored in. I chose C:\GITProjects
2) Right click on the folder GITProjects >> Clone a repository
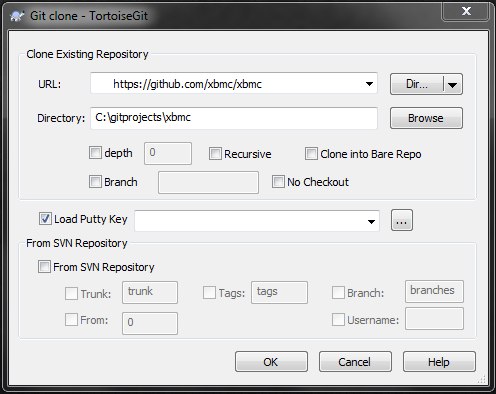
3) Lets take the example of the full XBMC source code so we type into the https://github.com/xbmc/xbmc URL field. And C:\GitProjects\XBMC into the Directory field.
Forking a Repository
Making a copy of an existing project on the GITHub website and Downloading it to your local computer.
This allows you to upload commits and pull requests in the future without effecting the original repository
1) Create a folder on your computer for the projects to be stored in. I chose C:\GITProjects
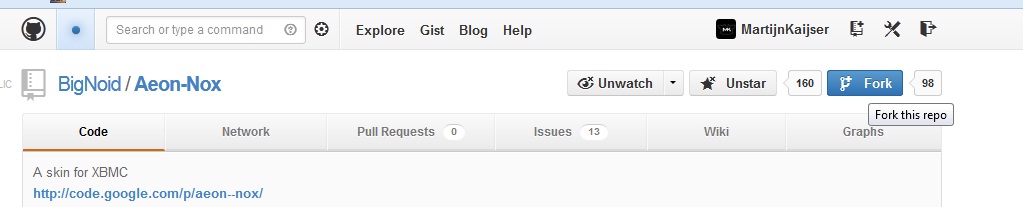
2) Go to the GitHub website and find the project you want to fork. Then click on the Fork button in the top right corner. It should only take a few seconds and then the project will show in your own GitHub area.
3) Right click on the folder GITProjects >> Clone a repository
4) Now simply enter the URL of the new fork you have created and a local folder to put it in.
Creating a new Project
Uploading an entire new project from your local computer to GitHub
1) Got to github.com and create a new repository
2) Go to your local computer and create a new directory for your project. For example c:\GITprojects\MyProject. Make sure it is empty for now.
3) Copy the URL of the repository you created into the clipboard memory
4) Right click on the root "Gitprojects" folder >> Clone a repository. Your URL should be auto completed and so should the source. Click OK and wait for it to set the repository up.
5) Now copy any project source code you have written into the "MyProject" folder.
6) Right click on "MyProject" >> Gti Commit -> Master. Type in something like "initial commit" in the message box. Now click on the "ALL" button to select all your files to upload.
7) After the files are uploaded, click the push button to finalize the operation. That's it, all your files should now be stored in the on-line GitHub repository
Committing a piece of code to your own repository
Commiting a small piece of code to your own project on GitHub
1) Copy or edit your code in the c:\Github\Project1 folder
2) Go back to the root of c:\Github and right click on the "Project1" folder -> Git Commit -> "Master"
3) In the box write a commit message and make sure you have selected the files that are added or changed with the tick box.
4) Once the files have been commited, hit the PUSH button to upload them to the GitHub website.
5) You can now check the files are uploaded by browsing to the github website and specific repository.
Creating a pull request
Packaging up a new feature or code change for others to review and comment on
1) Navigate to the github website and your personal repository (usually this will be a fork of another repository)
2) Commit and push any changes to your personal version of the code.
3) Once you have uploaded your changes you can go to the repository and click "Pull Request"
4) Add a name for the PR and make any comments. Github should automatically find and changes in the file.
5) Once your pull request is complete, people will be able to comment on it and merge it.
Squashing commits into one
Squashing a number of commits down to a single commit so its easy to review and keep track of
1) Assuming you have a couple of commits, right click on the repository >> tortoise >> show log
2) Select the commits right click >> combine to one commit
3) Right click on the repository >> tortoise >> Push.
4) Check the box that says force overwrite existing branch
Resetting your local master
Resetting your local master back to a remote master
1) Right click on the repository >> Switch to master
2) Right click on the repository >> Show log
3) Change to the XBMC remote master repository in the top left hand corner
4) Right click on the latest commit >> Reset
5) Choose hard reset (warning this will delete any local changes)
Amend to last Commit
If you make a commit then have to add something to it
1) Right click on the repository >> Commit (this will be the 2nd commit)
2) Check tickbox that says "Ammend to last commit"
3) Check tickbox that says "Force push" to your own repository
Testing someone elses pull request
Pulling down a set of patches that you can apply to your local repository and test out
coming soon...


Here's a little guide to starting off from the perspective of a n00b while attempting to put it in plain English.
I'm assuming you have signed up for github and are working on Windows with TortoiseGIT installed. Other platforms and Git tools should work in a similar way.
Cloning a Repository
Copying an existing project from the GITHub website and all its code to your local computer.
This is usually used when you want to test a one time copy of a project on your local computer without making any changes in the future
1) Create a folder on your computer for the projects to be stored in. I chose C:\GITProjects
2) Right click on the folder GITProjects >> Clone a repository
3) Lets take the example of the full XBMC source code so we type into the https://github.com/xbmc/xbmc URL field. And C:\GitProjects\XBMC into the Directory field.

Forking a Repository
Making a copy of an existing project on the GITHub website and Downloading it to your local computer.
This allows you to upload commits and pull requests in the future without effecting the original repository
1) Create a folder on your computer for the projects to be stored in. I chose C:\GITProjects
2) Go to the GitHub website and find the project you want to fork. Then click on the Fork button in the top right corner. It should only take a few seconds and then the project will show in your own GitHub area.

3) Right click on the folder GITProjects >> Clone a repository
4) Now simply enter the URL of the new fork you have created and a local folder to put it in.
Creating a new Project
Uploading an entire new project from your local computer to GitHub
1) Got to github.com and create a new repository

2) Go to your local computer and create a new directory for your project. For example c:\GITprojects\MyProject. Make sure it is empty for now.
3) Copy the URL of the repository you created into the clipboard memory
4) Right click on the root "Gitprojects" folder >> Clone a repository. Your URL should be auto completed and so should the source. Click OK and wait for it to set the repository up.
5) Now copy any project source code you have written into the "MyProject" folder.
6) Right click on "MyProject" >> Gti Commit -> Master. Type in something like "initial commit" in the message box. Now click on the "ALL" button to select all your files to upload.
7) After the files are uploaded, click the push button to finalize the operation. That's it, all your files should now be stored in the on-line GitHub repository

Committing a piece of code to your own repository
Commiting a small piece of code to your own project on GitHub
1) Copy or edit your code in the c:\Github\Project1 folder
2) Go back to the root of c:\Github and right click on the "Project1" folder -> Git Commit -> "Master"
3) In the box write a commit message and make sure you have selected the files that are added or changed with the tick box.
4) Once the files have been commited, hit the PUSH button to upload them to the GitHub website.
5) You can now check the files are uploaded by browsing to the github website and specific repository.
Creating a pull request
Packaging up a new feature or code change for others to review and comment on
1) Navigate to the github website and your personal repository (usually this will be a fork of another repository)
2) Commit and push any changes to your personal version of the code.
3) Once you have uploaded your changes you can go to the repository and click "Pull Request"
4) Add a name for the PR and make any comments. Github should automatically find and changes in the file.
5) Once your pull request is complete, people will be able to comment on it and merge it.
Squashing commits into one
Squashing a number of commits down to a single commit so its easy to review and keep track of
1) Assuming you have a couple of commits, right click on the repository >> tortoise >> show log
2) Select the commits right click >> combine to one commit
3) Right click on the repository >> tortoise >> Push.
4) Check the box that says force overwrite existing branch
Resetting your local master
Resetting your local master back to a remote master
1) Right click on the repository >> Switch to master
2) Right click on the repository >> Show log
3) Change to the XBMC remote master repository in the top left hand corner
4) Right click on the latest commit >> Reset
5) Choose hard reset (warning this will delete any local changes)
Amend to last Commit
If you make a commit then have to add something to it
1) Right click on the repository >> Commit (this will be the 2nd commit)
2) Check tickbox that says "Ammend to last commit"
3) Check tickbox that says "Force push" to your own repository
Testing someone elses pull request
Pulling down a set of patches that you can apply to your local repository and test out
coming soon...